Blood Glucose Level Chart

Leveraging a blood glucose level chart is a great way to understand how well your body is maintaining your blood glucose levels.
Contrary to popular belief, understanding the body's sugar or glucose levels through a blood sugar level chart is not only for folks who have diabetes. As the matter of fact, it can be an early warning if the body will develop diabetes and in some instances, can be the key to preventing diabetes mellitus. However, even with blood sugar chart, maintaining a healthy blood sugar or glucose level can still be a difficult task for some, depending on how their body utilizes and responds to glucose.
Blood Glucose Level Chart
In normal cases, blood glucose, which is the main means of transporting energy to all of the body's cells, is maintained and regulated through insulin - which in turn, is the chemical that transports blood sugar into the various cells of the body.
Whenever food that contains more than normal sugar levels enter the body stream, extra insulin is produced to lower the blood stream's glucose ratio so that it can accommodate the extra amount of sugar going in. Medical experts agree that this makes the body a little bit more hyperactive as the body cells receive a sudden boost of energy.
This ability to maintain the body's sugar ratio significantly diminishes when one develops diabetes. Or the pancreas completely stops or drastically reduces its insulin production. In these cases, charting blood sugar levels and creating a blood glucose level chart gains a paramount importance as the body stops automatically using up "extra" glucose in the bloodstream.
Too much blood sugar thickens the blood and damages small blood vessels in the body. The first victim is often the eyes since there are quite a lot of small blood vessels lining your eyes. Hence, keeping a blood glucose level chart is vital to further prevent damages to blood vessels and other serious complications that can arise due to diabetes.
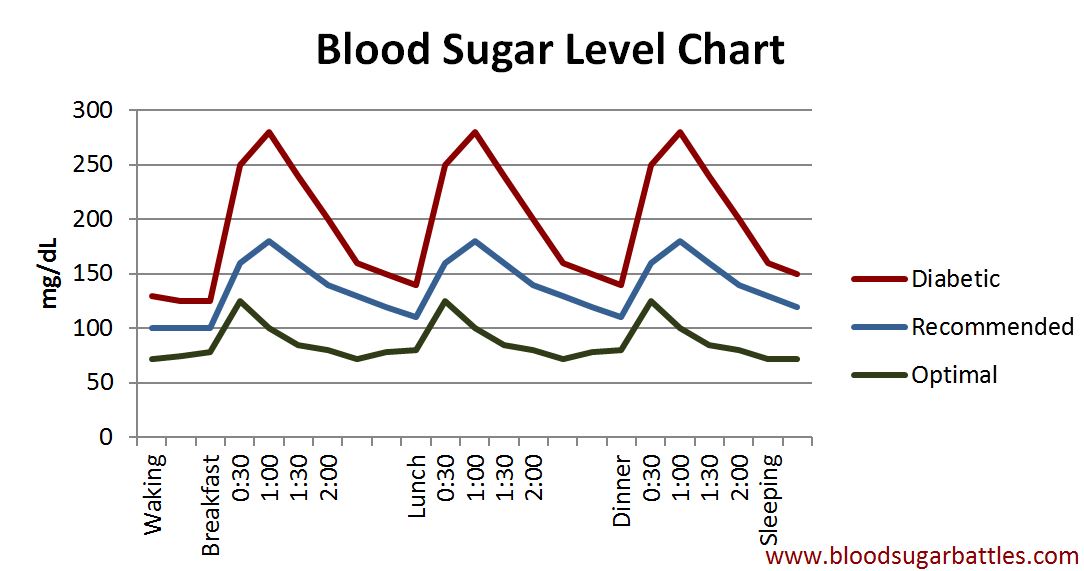
A normal person's body glucose ratio normally ranges in between 4 to 8 mmol/l. This unit measures how much glucose or sugar is present per liter of blood plasma. As said, your body adjusts to the many factors affecting the blood sugar or glucose in the body.
Hence, your levels will vary depending on how far you are from your meals or what your mood is. Your normal body glucose level before meals is somewhere between 4 to 7 mmol/l. 90 minutes after a meal as your body begins to intake digested food, it goes up to just below 10 mmol/l. Before and during your sleep, as your body rests, your body sugar should stabilize at 8 mmol/l.
Going below these levels is harmful too. This condition known as hypoglycemia or low blood sugar levels can lead to coma or fainting. Mildly, this causes clumsiness. Severely, it can sometimes lead to death. If asleep, hypoglycemia or low blood sugar can cause nightmares and feeling tired or confused after waking up.
In normal people, whenever the body's glucose level goes dangerously low, it triggers hunger, thus prompting the person to eat to raise their blood sugar levels. The body still responds and prevents this condition. However, there are instances when even people with “normal” blood sugar levels have trouble and the body can't maintain a constant blood glucose level. An example is when the person has a habit of skipping meals, the body would not have enough glucose stored in the liver and in the muscles, thus causing sleepiness or weakness.
In the end, maintaining good sugar levels in the body is important not only to maintain good health
but in keeping the body in optimum shape and the mind in optimum attention. Leveraging a blood glucose level chart like the one above is important to keeping you on track.


New! Facebook Comments
What do you think? Share your thoughts below...