All About Fasting Blood Sugar
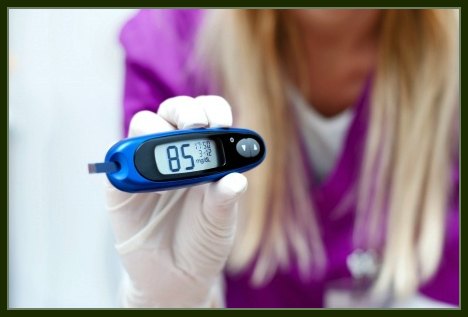
Simply put, fasting blood sugar is a measurement of the sugar levels in your blood after you have refrained from eating or drinking anything other than water for at least eight hours. Unless you have had blood sugar issues in the past, you likely don’t know what your fasting blood glucose is. Typically fasting blood sugar is measured first thing in the morning. If you want to, you can purchase a blood glucose monitor and measure your own blood sugar levels first thing in the morning.
Why is your fasting blood sugar level important to know?
When you don’t eat for a period of time your body releases a hormone called glucagon that increases blood glucose levels in your body. If you don’t have diabetes, your body will produce Basal insulin to rebalance the increased glucose levels. However, certain people don’t produce enough insulin to rebalance their blood sugar. This causes their blood sugar levels be too high. These people typically have type 1 diabetes. Other people release the insulin but their body is not able to effectively use the insulin due to a problem called insulin resistance. Although it is for a different reason, these people also have blood sugar levels that are too high. They typically have type 2 diabetes.
Why is it important to know what your fasting blood glucose levels are?
When you test your fasting blood glucose levels, you are checking your pancreas’s ability to produce basal insulin. The purpose of basal insulin release is to keep a small amount of insulin available in your bloodstream at all times via small pulses that occur every few minutes throught the day and night.
Remember, before your cells can use the glucose in your blood, it must be transported inside the cells. Insulin is the hormone that makes this happen. Maintaining a steady supply of insulin is important since it allows the cells in your body to utilize the sugar in your blood whenever they need it.
Some of the symptoms that indicate that you may be having blood sugar problems are:
- Shakiness
- Unexplained sweating, chills and clamminess
- Irritability or impatience, especially before meals
- Foggy thinking
- Dizziness
- Fatigue
Situations where it is important to know what your fasting blood glucose levels are:
- You are diabetic
- You are pregnant
- You have been diagnosed with metabolic syndrome
- You have been told that you are insulin resistant
- You are taking certain medications
- You have certain health conditions (like adrenal fatigue)
How is fasting blood sugar measured?
Fasting blood glucose is typically measured using a fasting glucose test at your doctor’s office. Your doctor will typically ask you to come into the office first thing in the morning. They will want you to verbally confirm that you haven’t eaten or drunk anything except for water for at least eight hours. Then they will take a sample of your blood and send it to the lab to determine what your fasting blood glucose level is. If you want, you can perform this test on your own using a blood glucose monitor and testing your own blood first thing in the morning.
Fasting Blood Sugar Test Results
Here is how to interpret your test results:
- Optimal: 70-85 mg/dL (3.9- 4.72 mmols/L) **
- Normal: 70 -99 mg/dL (3.9 - 5.5 mmols/L)
- Prediabetic: 100 - 130 mg/dl (5.1 - 7.2 mmol/L)
- Diabetic: greater than 130 (7.2 mmol/L)
** Research has shown that people with fasting blood glucose over 92 mg/dL are much more likely to develop diabetes within a decade, suggesting that the doctor recommended normal blood sugar levels are not optimal. Reference: "Normal fasting plasma glucose levels and type 2 diabetes in young men." Tirosh A et al. N Engl J Med. 2005 Oct 6;353 (14):1454-62
Also note that in 1998 they lowered the fasting blood sugar levels. Prior to 1998 people were not considered to be diabetic unless their fasting blood sugars were over 140 mg/dL. As a result, you must use caution when interpreting older studies because many of the people that were considered to be nondiabetic in older studies were actually diabetic.


New! Facebook Comments
What do you think? Share your thoughts below...