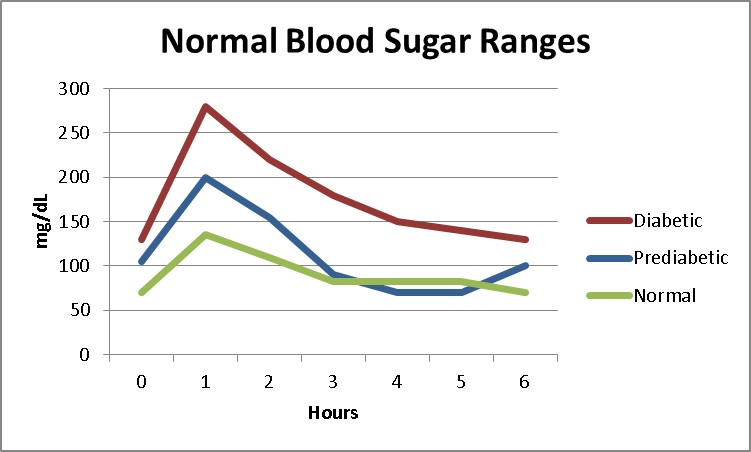
Blood Sugar Testing
Blood sugar testing is an important part of diabetes care. It is also critical for diagnosing metabolic syndrome, insulin resistance, gestational diabetes and to determine whether your body is having trouble managing its blood sugar levels.
There are a number of ways to measure blood glucose including:
Fasting Blood Sugar Test (FBS)
Often the first test that is performed to diagnose diabetes or prediabetes, the fasting blood glucose test is conducted after you have not eaten for at least 8 hours. Learn more about fasting blood sugar.
2-hour Postprandial Blood Sugar Test
This test measures blood glucose exactly 2 hours after you start eating a meal. This test is most often used to see if someone with diabetes is taking the right amount of insulin with their meals. Learn more about this test and what normal and optimal results are.
Random Blood Sugar Test (RBS)
This test measures your blood sugar regardless of when you ate
last. To make sense of how your body is processing blood sugar, several random measurements are often taken throughout the day. This is the best test for determining how your body does processing certain types of food and allows you to determine what foods cause your blood glucose to spike. Learn all about normal blood sugar ranges, why yours my not be ideal and what you can do about it.
Oral Glucose Tolerance Test
This is another test that is typically used to diagnose diabetes, prediabetes and gestational diabetes. Your blood sugar is measured at certain intervals (often every 30 minutes for two hours) after you drink a prescribed amount of glucose.
The oral glucose tolerance test is most often used to test for gestational diabetes. Learn more about:
- Gestational diabetes testing
- Problems caused by gestational diabetes
- How to manage gestational diabetes
- What to eat to maintain your blood sugar levels naturally to protect both you and your baby.
Hemoglobin A1c Test (Glycohemoglobin)
This test reflects your average blood sugar levels over the past two or three months. It measures how much glucose is stuck to your red blood cells. It is useful in determining how well your blood sugar levels are controlled either naturally or by diet and/or medicine. The American Diabetes Association suggests that a normal result for this test is 7% or an estimated average blood sugar level of 154 mg/dL.
Urine Glucose Test
Urine glucose tests are not as accurate as blood glucose tests and should only be used when it is impossible to perform a blood test.
All of the above tests can be ordered and/or performed by your doctor. Several you can perform on your own and you don’t even need to be diabetic to learn whether or not your body is processing glucose appropriately. All you need to do is purchase a blood glucose meter and follow the instructions below.
Blood Sugar Testing - The Short Version
All blood sugar meters are slightly different, so always refer to the user’s manual and instructions for your particular meter.
These steps should work with the majority of meters.
- Wash your hands
- Insert a test strip into your blood glucose meter
- Use a lancing device on the side of your fingertip to get a drop of blood (a spring loaded lancing device is best)
- Touch and hold the edge of the test strip to the drop of blood for a few seconds until your glucose monitor indicates that it has received it and has started the test
- Wait for the result, your blood sugar level will appear in the meter’s display
- Document your results
Blood Sugar Testing - Steps with Explanation
The following is the best way we have found to test our blood sugar. These blood sugar testing tips “come from the trenches”. It has been our experience that the easier and more comfortable we make testing, the better we get at managing our blood sugar.
Here are the steps:
- Open your kit, insert a new lancet into your lancet device (if needed). You can reuse your lancets if you are the only one using your device. Never share a lancet! While officials will report that lancets get duller with each use, many people report that reusing the same lancet is more comfortable than using new ones. Most people we know use the same lancet for a month or two. Adjust the depth of your lancet if necessary, we use the shallowest depth we can that still result in a drop of blood, starting with the “1” on most lancets. You can decide what you think is the best depth and how often you want to change lancets over time.
- Insert a new test strip into your meter
- Obtain a drop of blood by using your lancet device on the side of your finger. Pinky and ring fingers seem to provide the best blood flow at the least possible lancet setting. Some people like testing on the back of their finger under their nail, but others find this spot to be painful. Don’t test on the pad of your finger. There are lots of nerves there and it hurts. Some meters allow you to test on your arm. We find it to be painful and avoid this option unless there is some reason we just can’t test on our fingers. Arm testing also results in blood sugar readings that lag behind what you would have gotten if you had tested your finger due to the increased interstitial fluid in your arm. We also don’t bother using an alcohol wipe before testing. Not only does that dry out and toughen your skin, but it is unnecessary according to those in the know like Dr. Bernstein. He reports that neither he nor any of his patients has ever developed an infection after testing without alcohol. If your hands are dirty, was them before testing, but don’t use alcohol. If you see a surprisingly high reading, wash your hands and try again since an unexpectedly high reading often occurs due to a tiny amount of sugar on your finger.
- Place the test strip in the appropriate position (according to your device’s instructions) to “suck” up the drop of blood and wait the prescribed amount of time for your blood sugar level to display.
- Document your results in a journal. You can use the booklet that came with your meter, a piece of paper you keep with your meter or one of the new smartphone applications.
Keep your meter with you and test at regular intervals. Read about ideal blood sugar ranges and our tips for how often to test for more information about when and why to test.
More Information
- High Blood Sugar
- Low Blood Sugar
- Tracking Your Blood Sugar
- Fasting Blood Sugar
- Managing your Blood Sugar


New! Facebook Comments
What do you think? Share your thoughts below...