An Ideal Blood Sugar Range

According to the International Diabetes Federation, a normal blood sugar range for people without diabetes and who are not fasting should be between 82 mg/dL (4.4 mmol/L) and 110 mg/dL (6.1 mmol/L) with 82 mg/dl being optimal.
The reason that blood sugar is typically expressed as a range is because it is highly individual and it fluctuates throughout the day based on what you eat, how much exercise you
get, your genetics, how old you are and due to certain medical conditions like adrenal fatigue. When it comes to blood sugar, it is just as important to know how high your blood sugar goes after a meal as it is to know what your typical blood sugar range is before meals
For this reason, to get a good idea regarding what range your blood sugar typically fluctuates between, it is best to test your blood at the following times:
First thing in the morning before your first meal
- Before eating
- 1/2 hour after eating
- 1 hour after eating
- 2 hours after eating.
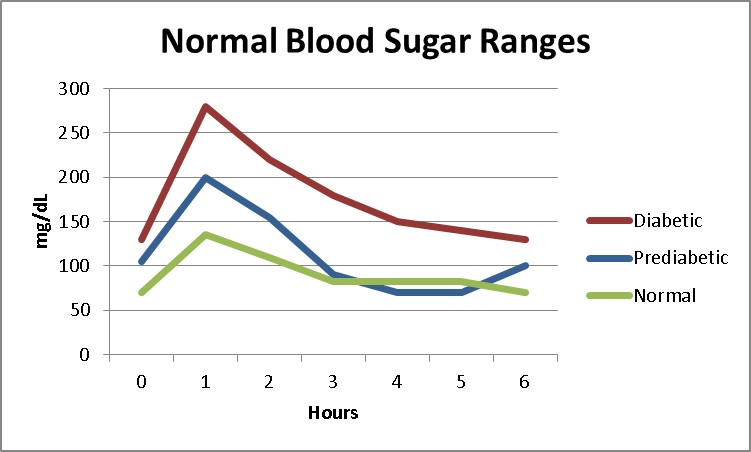
Normal Blood Sugar Range
Based on information from a variety of sources like the American Diabetes Association, the International Diabetes Federation, and the National Institute for Clinical Excellence (NICE).
- Fasting range between 70 and 100 mg/dL (3.9 to 5.6 mmol/L )
- Optimal non-fasting range before a meal is less than 100 mg/dL (5.5 mmol/L )
- When operating normally the body restores blood sugar levels to a range of 82 to 110 mg/dL (4.4 to 6.1 mmol/L) within two hours after eating
- Shortly after a meal your blood glucose level may rise temporarily up to 140 mg/dL (7.8 mmol/L) but should not exceed 180 mg/dL (10 mmol/L)
Diabetic Blood Sugar Range
The American Diabetes Association recommends that diabetics keep their blood sugar within the following ranges:
- A1C: 7% or eAG of 154 mg/dL
- Blood Test result of 70-130 mg/dL before a meal (preprandial plasma glucose)
- Blood Test result of less than 180 mg/dL 1-2 hours after a meal (Postprandial plasma glucose)
Why is it important to know your blood sugar range?
Blood sugar, also known as glucose, is a monosaccharide and one of your body’s primary sources of energy. The actual amount of glucose in your blood and body fluids is very small, slightly less than two typical American restaurant sugar packets or approximately one teaspoon.
If your blood sugar gets too low, also known as hypoglycemia, then there isn’t enough glucose in your blood to feed your brain and other tissues. When this happens, often due to skipped meals or after excess sugar consumption, it becomes hard for people to think and they may feel shaky. People are generally considered hypoglycemic if their blood sugar consistently falls below 70 mg/dl (4 mmol/L).
High blood sugar, also known as hyperglycemia, happens when too much glucose is circulating in your blood. Typically you are considered hyperglycemic if your blood sugar goes above 250-300 mg/dl (15-20 mmol/L)
How can you determine what your blood sugar ranges are?
Two ways to get an initial idea of what your blood sugar levels are:
- Blood Sugar Self Test using a Glucose Meter
- The A1C test and what it measures
A1C Test
An A1C test will reflect your average blood sugar level for the past two or three months For the A1C test, your doctor or a lab will need to take a blood sample.
How to test with a glucose monitor
You can perform your own blood sugar test using a glucose meter purchased at a pharmacy, but it will only tell you what your blood sugar level is at the time of the test. Therefore if you want to get an accurate assessment of your blood sugar status, you will need to test your blood throughout the day for at least a couple days.
Read step by step instructions for measuring your blood glucose with a glucose monitor
What if my blood sugar is outside of the normal range?
If your blood sugar falls outside the normal blood sugar range using the above testing methods, then you will need to do some further testing. The two tests your doctor is likely to perform are:
- Fasting blood glucose test
- Glucose tolerance test
A fasting blood glucose test measures your blood sugar levels after at least eight hours of fasting. Typically is a fasting glycemia test is done first thing in the morning. As we mentioned above, you can test your own blood glucose levels first thing in the morning and get a good idea of what your fasting blood sugar levels are.
A glucose tolerance test involves drinking a prescribed amount of sugar (usually an orange syrup) and then being tested at half hour intervals for two hours to see how effectively your body metabolizes sugar. If, after two hours, your blood sugar level is under 140 mg/dL (7.8 mmol/L) then you are considered normal. You will be considered to have impaired glucose metabolism if your results are between 141 mg/dL and 200 mg/dL (7.9 mmol/L and 11.1 mmol/L). You will be likely be given a diagnosis of diabetes if your blood glucose remains over 200 mg/dL (11.1 mmol/L) two hours after you drink the sugar solution.


New! Facebook Comments
What do you think? Share your thoughts below...