Normal Blood Sugar Range

For the majority of healthy individuals, a normal blood sugar range is:
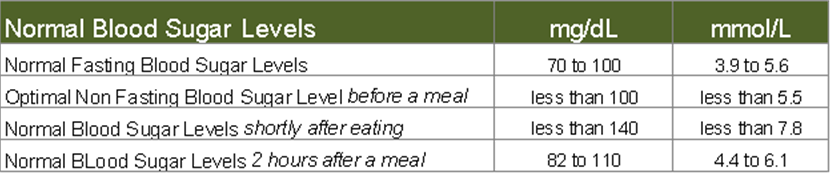
- Fasting range between 70 and 100 mg/dL (3.9 to 5.6 mmol/L )
- Optimal non-fasting range before a meal is less than 100 mg/dL (5.5 mmol/L )
- When operating normally the body restores blood sugar levels to a range of 82 to 110 mg/dL (4.4 to 6.1 mmol/L) within two hours after eating
- Shortly after a meal your blood glucose level may rise temporarily up to 140 mg/dL (7.8 mmol/L) but should not exceed 180 mg/dL (10 mmol/L)
Why do you need to know if your blood sugar is normal?
Not everyone agrees what a normal blood glucose range is. The ranges promoted by the American Diabetes Association, National Institute for Clinical Excellence (NICE) and International Diabetes Federation, to name just a few, are all different.
According to the International Diabetes Federation, a normal blood sugar range for people without diabetes and who are not fasting should be between 82 mg/dL (4.4 mmol/L) and 110 mg/dL (6.1 mmol/L) with 82 mg/dl being optimal.
The American Diabetes Association promotes the following ranges for most nonpregnant adults with diabetes:
- Before a meal (preprandial plasma glucose): 70-130mg/dL
- 1-2 hours after beginning f the meal (Postprandial plasma glucose): less than 180 mg/dL
The National Institute for Clinical Excellence (NICE) recommends the following blood glucose ranges for healthy individuals
- Normal blood glucose level: about 72 mg/dL (4 mmol/L)
- Before a meal (pre prandial): 72 - 106 mg/dL (4.0 to 5.9 mmol/L)
- 2 hours after meals (post prandial): 140 mg/dL (under 7.8 mmol/L)
Not only do the experts not agree on what a normal blood sugar range is, you as an individual have a challenge determining if your blood sugar levels are normal because your blood sugar levels can vary widely on a given day depending on what you eat as well as other health factors like exercise, fatigue, illness, adrenal health and how hydrated you are.
You may be within the normal blood glucose range the majority of the time, but outside of it a certain percentage of the time. Because what you eat is really the biggest factor that effects your blood sugar levels, normal blood sugar ranges are reported based on how long it has been since you have eaten.
According to the American Diabetes Association, the normal blood glucose range for a given individual may vary based on a number of factors like:
- If you have diabetes and for how long
- Your age
- Certain medical conditions
- Genetic heritage
- Individual patient considerations like hypoglycemia unawareness
Optimal Normal Blood Sugar Range
We believe that the following blood sugar ranges are optimal for healthy individuals based on information from a variety of sources like those listed above and numerous books on the topic.
Please note:
The international standard way of measuring blood glucose levels are in terms of a molar concentration, measured in millimoles per litre (mmol/L).
However, the United States and many other countries express glucose concentrations in terms of milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL). You can convert mg/dL to mmol/L by dividing by 18.0 g/dmol (the molar mass of glucose). For example you can convert 90 mg/dL to millimoles per litre by dividing by 18 to get 5.0 mmol/L.
Why are blood sugar ranges important?
Understanding normal blood glucose ranges and knowing what your blood sugar levels typically are is important because maintaining normal blood sugar is important to your overall health and longevity. There are numerous health conditions associated with both chronic low blood sugar as well as high blood sugar.


New! Facebook Comments
What do you think? Share your thoughts below...